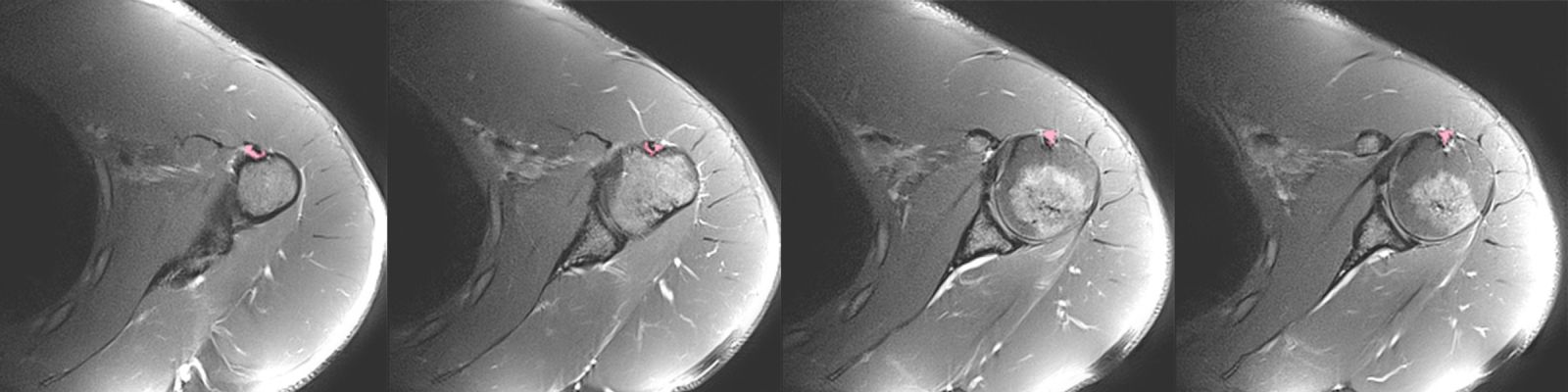
Shoulder Tendenitis
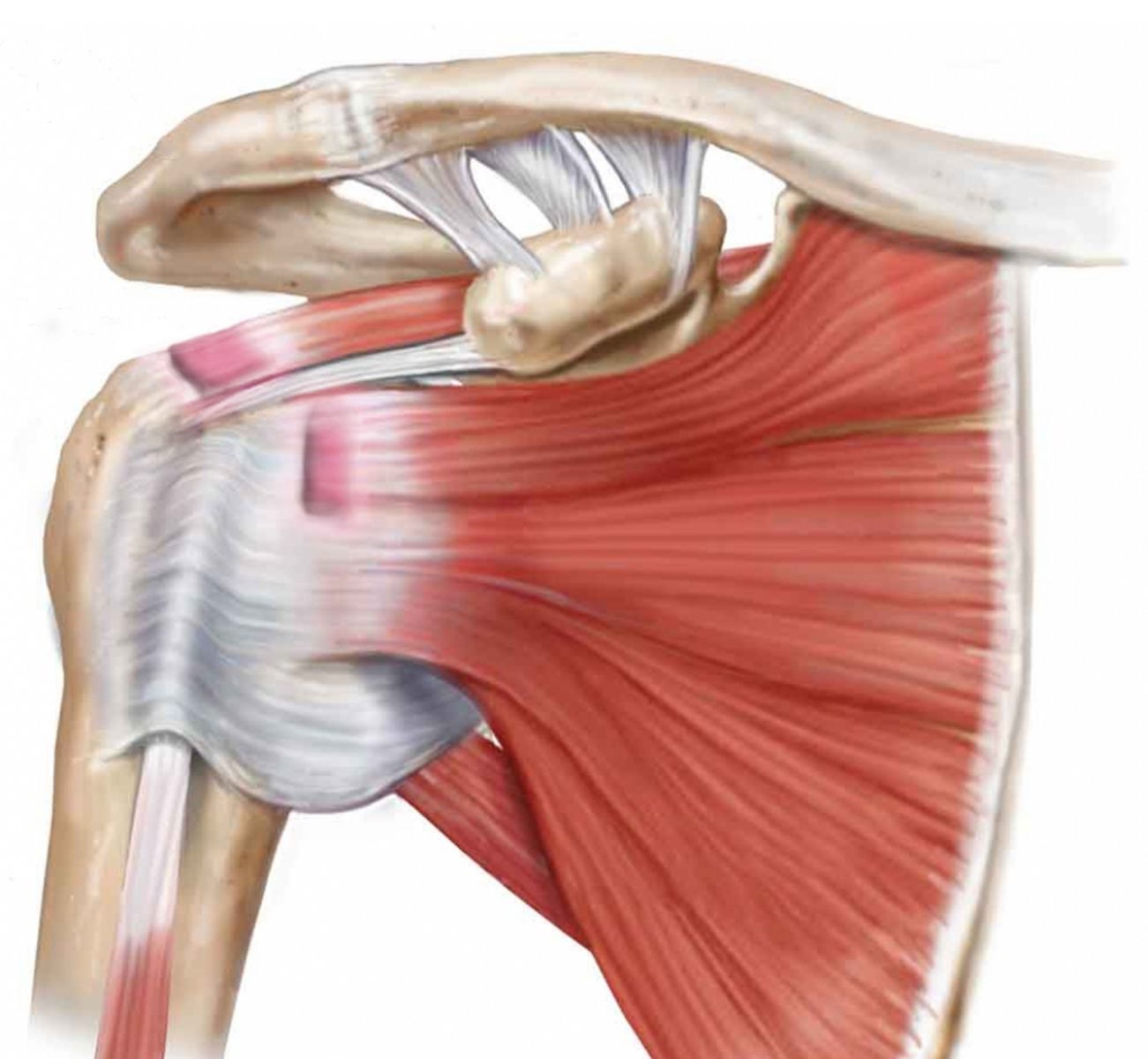
They are inflammations that occur in the shoulder rotating cuff muscles and the biceps tendon muscle that joins the shoulder joint. Painful and movement-limiting shoulder tendinitis usually occurs after strenuous activities, falls or long-term chronic trauma. Calcific tendonitis, which occurs as a result of the accumulation of calcium crystals in the shoulder tendons without any reason, can be evaluated in this context.
Şikayet
There are movement restrictions and pain that may be reflected in the arm when using the arm and lifting weights. These pains, which become more pronounced at night, may be in the form of aching and burning. The patient cannot lie on the problematic shoulder and may wake up with pain during position changes.
Muayene
By testing shoulder strength at different angles, shoulder muscles are evaluated separately and it is determined which tendon the complaint is in. In addition to shoulder strength, muscle strength and range of motion are checked. Muscle strength may be reduced or unchanged. Even if the patient does not lose strength, resistance may cause pain.
Teşhis
In the first stage, diagnosis can be made through examination and treatment can be given. If the complaint recurs or another problem is felt during the examination, additional examination may be requested. While calcium crystals seen on x-ray provide a diagnosis of calcific tendinitis, magnetic resonance can be used to determine whether there are additional problems in the muscles and the diagnosis of tendinitis is confirmed.
Tedavi
Tendinitis is an inflammation of the tendon and the first treatment is rest. Cold application and painkillers can be used to reduce pain and edema. If the complaint does not decrease after rest and medication, PRP or cortisone injections can be made into the shoulder. If the complaint persists, physical therapy is started. Surgery is not preferred except for persistent calcific tendinitis.