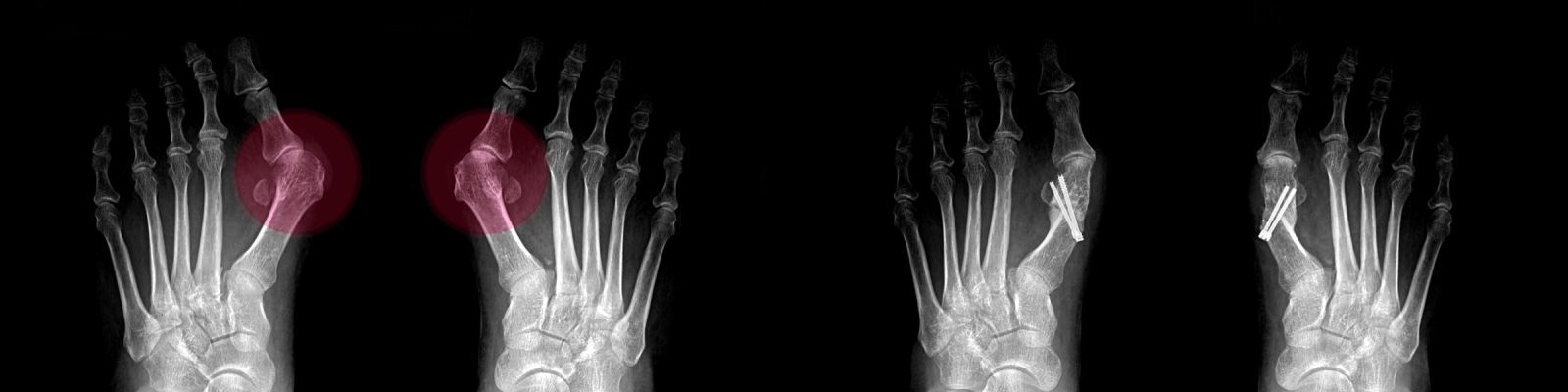
BIG TOE CURVATURE (HALLUX VALGUS)
It is a condition in which the big toe forms a severe angle with the first metatarsal bone. Thumb curvature cases, in which familial transmission is evident, may be painful or painless. The types of shoes used by the patient may increase the curvature problem or prevent its progression.
Şikayet
Complaints vary depending on the degree of deformation. Pain and deformities, decrease in walking distance, problems in choosing shoes and deterioration in the toe area of the shoes may be observed. If there is advanced deformity, the second and third fingers participate in the deformity and overlapping fingers occur.
Muayene
Defects in foot appearance are evident. The thumb is angled with the metatarsal bone to which it is attached, usually with a bone protrusion called a bunion. There may be collapses in the inner long axis of the foot. In cases of advanced deformation, the thumb may lift the second finger and a callus may form on the second finger.
Teşhis
After the examination, front and side x-rays are taken while in the standing position. According to the results, foot angles and degree of deformity are calculated.
Tedavi
Treatment is directed according to the patient's complaints. If there is a complaint of pain, the source of the pain should be questioned and the correct treatment should be chosen as a result of the examination. To relieve pain, support can be obtained from foot deformity insoles or silicone devices. Night splints and interfinger rollers can be used to prevent the progression of the deformity, but these require continued applications and may cause difficulties for patients.
Ameliyat
Correct planning should be made before the surgery, and the surgical method appropriate to the deformation of the foot should be determined. Since the postoperative care period is long, the patient must be fully informed about the surgery and his/her consent must be obtained. Hallux valgus operations, which are generally bone surgeries, may also include soft tissue surgery. The choice of anesthesia may be general anesthesia or spinal or epidural anesthesia applied from the waist. If epidural anesthesia is preferred, foot pain can be prevented for 2-3 days after the surgery with the help of a catheter placed in the waist area. Screw fixators are used in operations involving bone fractures. After the operation, the patient is taken to the service, is lifted up and pressed with the help of special shoes. After 2-3 days of hospitalization, the patient who does not have any wound problems is discharged. The stitches are removed approximately two weeks later. During the postoperative recovery period, the patient can step on his foot, but the foot is generally desired to be kept at a high level to prevent circulation problems. After the bone healing process, which takes 4-6 weeks, you can switch to normal shoes.